Researchers:
- Raluca Scarlat
- Sean McDeavitt
- Luis Ortega
Students:
- Primary Graduate: 3
- Undergraduate: 8
- Supporting Graduate: 4
Lab/Industry Interfaces:
- Kairos Power
- Thorcon Power
- Los Alamos National Laboratory
- Oak Ridge National Laboratory
- Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
- Argonne National Laboratory
- Copenhagen Atomics
- Moltex Energy
- TerraPower
- NRG Petten, Netherlands
- Kyushu Univeristy, Japan
Chemical Sensors

Motivation
- On-line, at-line, and off-line methods for characterization of salt composition and chemical state are limited.
- E.g.: oxide content quantification is a major challenge that impacts operations, and also impacts repeatability of experiments for corrosion and salt physico-chemical properties.
- Once a detection technique is demonstrated, sensor development efforts are an important step of technology transfer to MSR developers
Goals
- Proof-of-principle operation
- Development of data interpretation algorithms
- Development of calibration methods
- Identification of operational environments and design constraints
Approach
- Focus is on oxide content characterization, as a case study problem
- Demonstrate viability of electrochemical method, in FLiBe
- Demonstrate viability of IR optical methods, in FLiBe
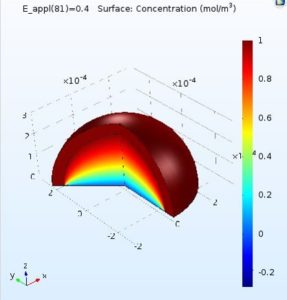
- COMSOL is used for chemical + CFD + thermal modeling to inform sensor design
- Generate salt sample library, and initiate round-robins for salt characterization with other groups

Waste Forms

Motivation
The advantages claimed for MSR waste production will only be realized if a credible waste immobilization/disposal pathway is established.
- These must be MSR-specific.
- Challenge to define without a well-defined “repository” specification.
Goal
NuSTEM focus is on fueled salt MSRs where fission products are dissolved in the salt.
- Presumes fission product (FP) generation during operation with batch removal.
- Work will be primarily done with surrogate FPs in FLiBe. (FLiNaK may be considered later).
- Selection of FLiBe principally due to its prominence as a fueled MSR Salt.
- Financial support for waste form task only enables a single salt for primary experimental work.
Approach
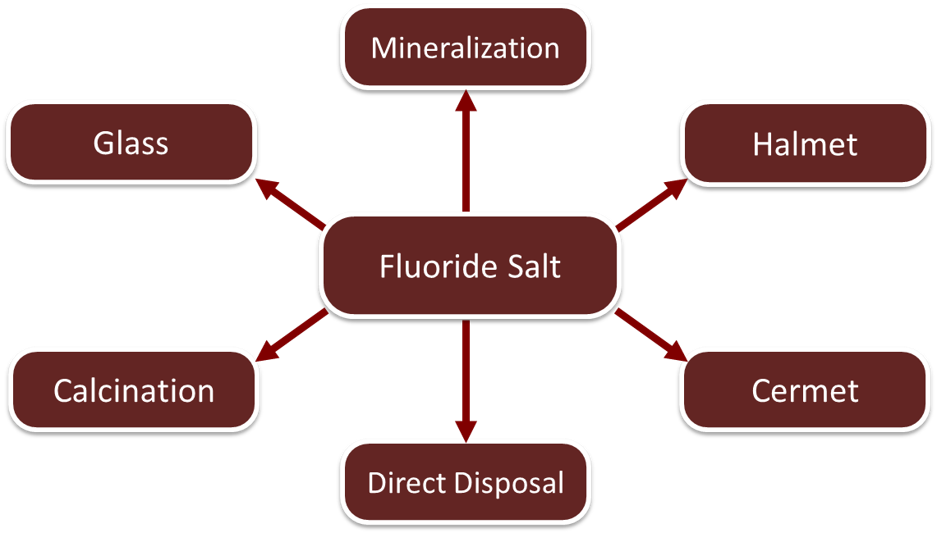
Immobilization of the various salt streams to create stable waste forms.
- Calcining (oxidation), vitrification (glass), ion exchange, mineralization have been explored in the past.
- Focus on calcination and mineralization methods.